Evolution of Holter Test in Cardiology
- 115 Views
- admin
- August 14, 2020
- Cardiology Health
The Holter test has come a long way since its inception in the 1960s. Originally developed by Norman J. Holter, an American biophysicist, the Holter test was a breakthrough in cardiac monitoring. It allowed for continuous, long-term monitoring of a patient’s heart activity, offering insights into heart rhythm abnormalities that were previously difficult to detect. Over the years, advancements in technology have transformed the Holter test into a more sophisticated and reliable diagnostic tool.n our fast-paced world, stress has become an unwelcome companion for many, impacting not only our mental well-being but also our physical health. Amidst the hustle and bustle, a powerful tool has emerged in the realm of healthcare: mindfulness. The practice of mindfulness, rooted in ancient traditions, is increasingly recognized for its profound effects on reducing the risk of heart disease. Let’s delve into the fascinating connection between mindfulness and cardiovascular health.
One of the key milestones in the evolution of the Holter test was the transition from analog to digital recording. In the early days, the test involved attaching multiple electrodes to the patient’s chest, which were then connected to a tape recorder. The patient had to carry the recorder, and the data had to be manually analyzed by a technician. This process was time-consuming and required significant effort.
However, with the advent of digital recording technology, the Holter test became more convenient and efficient. Digital recorders allowed for the automatic analysis of data, eliminating the need for manual interpretation. This not only reduced the burden on healthcare professionals but also improved the accuracy of the test results. Additionally, digital recording made it possible to store and transmit data electronically, enabling remote monitoring and consultation.
In recent years, the Holter test has undergone further advancements with the integration of wireless technology. Wireless Holter monitors have made it even more convenient for patients to undergo the test. These monitors are compact, lightweight, and can be worn discreetly, allowing patients to go about their daily activities without any hindrance. The wireless connectivity also enables real-time monitoring, as the data can be transmitted to a central monitoring station or healthcare provider’s office.
The evolution of the Holter test has not only made it more accessible and user-friendly but has also enhanced its diagnostic capabilities. With the introduction of advanced algorithms and software, the analysis of Holter test data has become more sophisticated. These algorithms can detect subtle changes in heart rhythm and identify patterns that may indicate underlying cardiac conditions. This level of accuracy has significantly improved the ability to diagnose arrhythmias and other heart rhythm abnormalities.
The advancements in Holter test technology have not stopped at monitoring devices and software. Researchers and engineers are constantly working on improving the sensors used in the test. These sensors are becoming more sensitive and accurate, allowing for better detection of electrical signals produced by the heart. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop wearable sensors that can provide continuous monitoring without the need for adhesive electrodes.
Overall, the evolution of the Holter test in cardiology has been remarkable. From analog tape recorders to wireless monitors and advanced algorithms, the test has undergone significant advancements. These advancements have not only improved the accuracy and efficiency of the test but have also expanded its applications, making it an indispensable tool in the diagnosis and management of cardiac conditions.
Advantages of Holter Test over Traditional Monitoring Methods
The Holter test offers several advantages over traditional methods of cardiac monitoring, such as the standard electrocardiogram (ECG). While a standard ECG provides a snapshot of a patient’s heart activity at a specific moment, the Holter test records the heart’s rhythm continuously over a prolonged period. This extended monitoring period allows for the detection of abnormalities that may not be captured by a single ECG.
One of the key advantages of the Holter test is its ability to identify arrhythmias. Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can have serious implications for a patient’s health. These rhythm disturbances may occur sporadically or intermittently, making them difficult to capture during a standard ECG. However, the Holter test’s continuous monitoring allows for the detection of these irregularities, enabling healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
Another advantage of the Holter test is its ability to evaluate the effectiveness of medications. Many cardiac conditions require long-term medication management, and the Holter test can provide valuable insights into how well these medications are working. By monitoring a patient’s heart activity while on medication, healthcare professionals can assess whether the treatment is effectively controlling arrhythmias or other abnormalities. This information is crucial for adjusting dosages or exploring alternative treatment options.
Additionally, the Holter test can be used to assess the risk of heart disease. By analyzing the heart’s rhythm over an extended period, healthcare professionals can identify subtle changes or abnormalities that may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular events. This information can help in risk stratification and guide preventive measures such as lifestyle modifications or additional diagnostic tests.
Furthermore, the Holter test allows for personalized treatment plans. The continuous monitoring and detailed data provided by the test enable healthcare professionals to tailor treatment strategies to individual patients. By analyzing the patterns and triggers of arrhythmias, healthcare professionals can recommend specific lifestyle modifications or interventions to reduce the frequency or severity of these abnormalities. This personalized approach improves patient outcomes and enhances their quality of life.
In summary, the Holter test offers several advantages over traditional monitoring methods. Its ability to detect arrhythmias, evaluate medication effectiveness, assess the risk of heart disease, and enable personalized treatment plans make it an invaluable tool in cardiology. By providing a comprehensive and detailed picture of a patient’s heart activity, the Holter test empowers healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and develop targeted treatment strategies.
How Holter Test Works
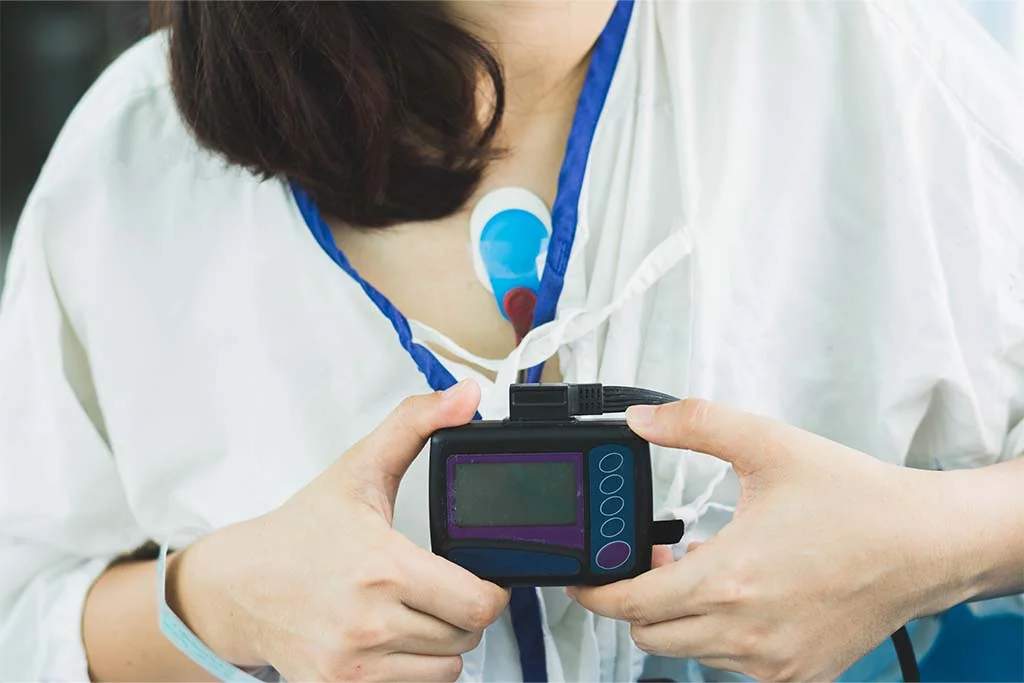
The Holter test is a noninvasive procedure that involves the continuous monitoring of a patient’s heart activity for an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. The test is performed using a Holter monitor, a portable device that records the electrical signals produced by the heart. This data is then analyzed to identify any abnormalities in heart rhythm.
The Holter monitor consists of several components, including electrodes, cables, and a recording device. The electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest using adhesive patches. These electrodes pick up the electrical signals generated by the heart and transmit them to the recording device via the cables. The recording device can be worn on a belt or carried in a pocket, allowing the patient to move around freely during the test.
During the Holter test, the electrodes continuously record the heart’s electrical activity. The signals are then converted into digital data, which is stored in the recording device. This data can be analyzed in real time or downloaded onto a computer for later analysis. The analysis involves the use of specialized software that processes the data and identifies any abnormalities or patterns that may indicate underlying cardiac conditions.
The Holter test is typically performed on an outpatient basis. Before starting the test, the patient’s skin is prepared by cleaning and lightly abrading it to ensure proper electrode contact. The electrodes are then attached to specific locations on the chest, usually in a configuration known as the 12-lead ECG. The patient is instructed to go about their daily activities as usual, avoiding any activities that may interfere with the monitoring process, such as swimming or taking a shower.
Once the monitoring period is over, the patient returns the Holter monitor to the healthcare facility. The data recorded by the device is then analyzed by a trained technician or healthcare professional using specialized software. The analysis involves reviewing the recorded data, identifying any abnormalities, and correlating them with the patient’s symptoms or medical history. The results of the analysis are then reported to the patient’s healthcare provider, who will interpret the findings and recommend appropriate treatment or further diagnostic tests if necessary.
The Holter test is a valuable diagnostic tool in cardiology, providing comprehensive and detailed information about a patient’s heart activity. It allows for the detection of arrhythmias, evaluation of medication effectiveness, assessment of the risk of heart disease, and the development of personalized treatment plans. By continuously monitoring the heart’s rhythm over an extended period, the Holter test offers insights that may go unnoticed during a standard electrocardiogram.
Recent Technological Advancements in Holter Test
In recent years, technological advancements have significantly enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of the Holter test. These advancements have transformed the way the test is conducted, analyzed, and interpreted, leading to improved patient outcomes and better diagnostic capabilities. Let’s explore some of the recent technological advancements in Holter test technology.
One of the key advancements in Holter test technology is the development of smaller and more lightweight monitoring devices. Traditional Holter monitors were bulky and cumbersome, making it uncomfortable for patients to wear them for extended periods. However, advancements in miniaturization and wearable technology have led to the development of compact and lightweight Holter monitors that can be worn discreetly and comfortably.
These smaller monitors not only improve patient comfort but also enable more accurate data collection. With improved sensor technology, these monitors can capture and record the heart’s electrical signals with greater precision. This leads to higher-quality data, which in turn improves the accuracy of the test results and the ability to detect subtle abnormalities in heart rhythm.
Another significant advancement in Holter test technology is the integration of wireless connectivity. Wireless Holter monitors allow for real-time monitoring and remote data transmission. The data recorded by the monitor can be transmitted wirelessly to a central monitoring station or a healthcare provider’s office, eliminating the need for the patient to physically return the device for data analysis.
Wireless connectivity also enables healthcare professionals to access the data and analyze it in real-time. This allows for immediate identification of any critical abnormalities or urgent medical interventions. Additionally, remote monitoring reduces the burden on healthcare facilities and enables more efficient use of resources, as healthcare professionals can monitor multiple patients simultaneously.
Furthermore, advancements in data analysis software have greatly improved the efficiency and accuracy of Holter test interpretation. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are now being used to analyze the vast amount of data generated by the test. These algorithms can detect complex patterns and subtle changes in heart rhythm that may indicate underlying cardiac conditions.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in Holter test analysis is also gaining traction. AI algorithms can learn from large datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions about a patient’s cardiac health. This AI-powered analysis can assist healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses, predicting the risk of cardiovascular events, and developing personalized treatment plans.
In summary, recent technological advancements have revolutionized the Holter test, making it more accurate, efficient, and convenient. Smaller and lightweight monitoring devices, wireless connectivity, and advanced data analysis software have significantly improved the test’s diagnostic capabilities. The integration of AI algorithms holds promise for further enhancing the accuracy of Holter test interpretation and improving patient outcomes.
Benefits of Advanced Holter Test Technology
The advancements in Holter test technology have brought about several benefits that have had a profound impact on the field of cardiology. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of advanced Holter test technology and how they have improved patient care and outcomes.
Improved Accuracy: Advanced Holter test technology, such as smaller and more sensitive sensors and advanced data analysis algorithms, has significantly improved the accuracy of the test. These advancements allow for the detection of subtle changes in heart rhythm that may go unnoticed during a standard electrocardiogram. The improved accuracy leads to more accurate diagnoses, better treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.
Early detection of arrhythmias: The Holter test’s continuous monitoring capabilities enable the early detection of arrhythmias, even those that occur sporadically or intermittently. By capturing these abnormalities over an extended period, healthcare professionals can make accurate diagnoses and recommend appropriate treatment plans. Early detection of arrhythmias allows for timely intervention and reduces the risk of complications.
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness: Advanced Holter test technology allows for the evaluation of the effectiveness of medications in controlling arrhythmias. By monitoring a patient’s heart activity while on medication, healthcare professionals can assess whether the treatment is effectively controlling the abnormal heart rhythm. This information is crucial for adjusting dosages or exploring alternative treatment options, leading to better medication management.
Assessment of Risk of Heart Disease: The Holter test provides valuable insights into a patient’s risk of heart disease. By analyzing the heart’s rhythm over an extended period, healthcare professionals can identify subtle changes or abnormalities that may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular events. This information can help in risk stratification and guide preventive measures such as lifestyle modifications or additional diagnostic tests.
Personalized Treatment Planning: The detailed and continuous data provided by the Holter test allows for personalized treatment planning. By analyzing the patterns and triggers of arrhythmias, healthcare professionals can recommend specific lifestyle modifications or interventions to reduce the frequency or severity of these abnormalities. This personalized approach improves patient outcomes and enhances their quality of life.
Convenience and Patient Comfort: Advanced Holter test technology has made the test more convenient and comfortable for patients. Smaller and lightweight monitoring devices are less intrusive and allow patients to go about their daily activities without hindrance. Wireless connectivity eliminates the need for physical device return, reducing the burden on patients and healthcare facilities.
Remote Monitoring and Consultation: The integration of wireless connectivity in Holter monitors enables remote monitoring and consultation. The data recorded by the device can be transmitted wirelessly to a central monitoring station or healthcare provider’s office. This allows for real-time monitoring and immediate identification of critical abnormalities or urgent medical interventions. Remote monitoring also reduces the need for frequent visits to healthcare facilities, increasing accessibility for patients.
In conclusion, advanced Holter test technology has brought about numerous benefits in the field of cardiology. Improved accuracy, early detection of arrhythmias, evaluation of medication effectiveness, assessment of the risk of heart disease, personalized treatment planning, convenience, and remote monitoring are among the key advantages. These benefits have improved patient care, enhanced diagnostic capabilities, and led to better outcomes for individuals with cardiac conditions.